AWS Centralized Traffic Mirror Solution
Introduction
The need for robust and real-time security monitoring has never been more critical. A recent client sought to mirror their network traffic to a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tool for AI analysis, without compromising data privacy or redundancy. A previously attempted solution involving a transient gateway led to a network outage, highlighting the need for a more resilient and scalable architecture.
The Solution: Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB)
I decided to employ the AWS Gateway Load Balancer (GWLB), recognizing its inherent benefits:
- Highly Available: GWLB offers a regional construct that helps in distributing traffic across multiple availability zones.
- Scalable: It automatically scales with the volume of network traffic.
- Non-Disruptive: By providing a single gateway for distributing traffic, it avoids bottlenecks and potential failures.
Architecture
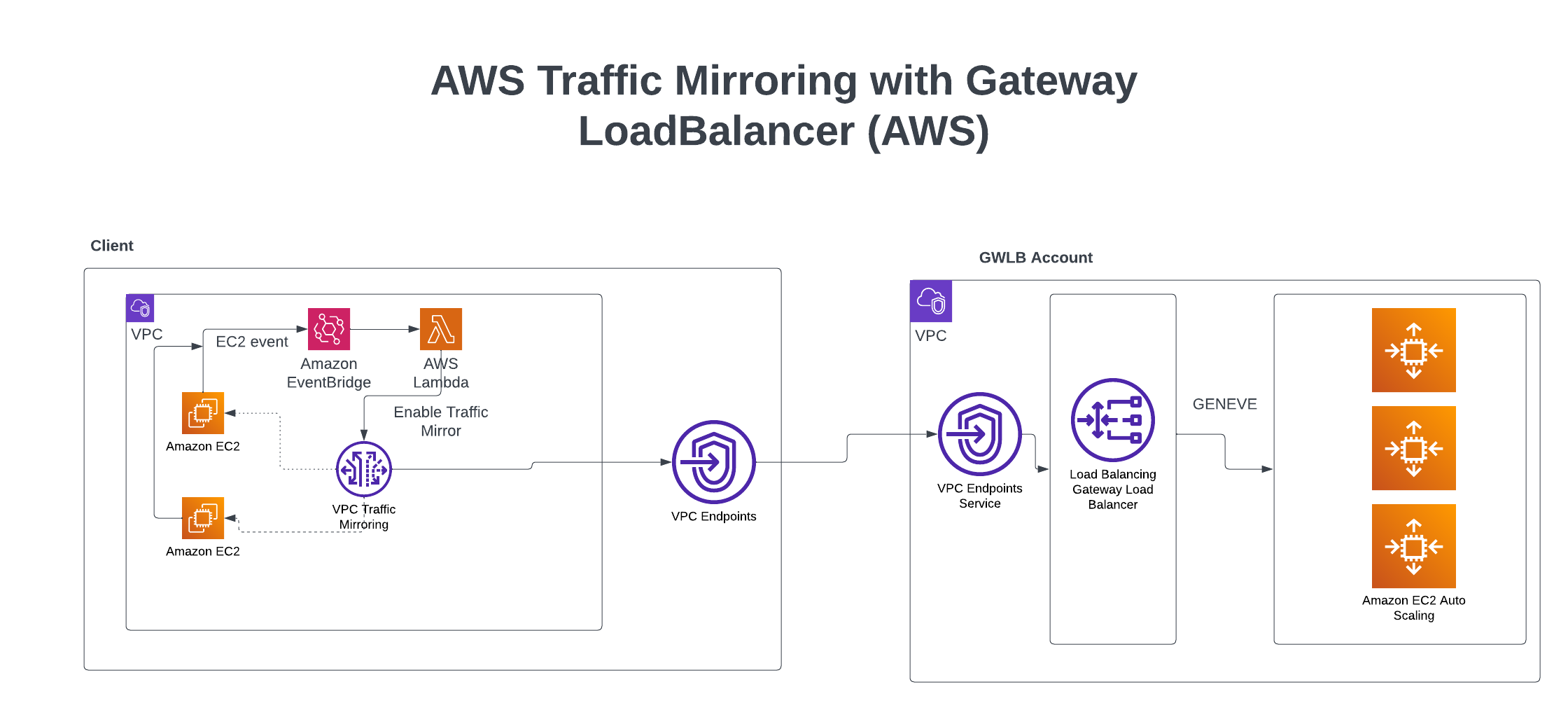
Central Account Configuration
- GWLB and EC2 Auto Scaling Group: A central account was configured with the GWLB, paired with an EC2 auto-scaling group, poised to receive the forwarded traffic from the GWLB.
- Traffic Forwarding with Geneve Protocol: The Generic Network Virtualization Encapsulation (Geneve) protocol was employed, designed to unify various encapsulation methods while retaining flexibility.
Client Accounts Configuration
- Choosing Correct EC2 Instances: Specific EC2 instances compatible with traffic mirroring (please confirm if t3 instances are suitable) were selected.
- VPC Endpoint Configuration: A VPC endpoint was created that targeted the GWLB VPC service endpoint in the GWLB account.
- Dynamic Traffic Filters and Targets: Instead of a static traffic session, a dynamic approach was adopted to account for the transient nature of EC2 instances. An all-encompassing traffic filter was employed, targeting all protocols.
- EventBridge and Lambda Integration: AWS EventBridge was configured to monitor EC2 behaviors (shutdowns, creation, termination, etc.). This acted as a trigger to AWS Lambda, creating or deleting traffic mirror sessions based on the instances' lifecycle events.
Automation with Terraform
All of the infrastructure was automated using Terraform, ensuring a repeatable and error-free deployment.
Conclusion
The solution elegantly met the client's requirements, providing a scalable, highly available, and non-disruptive system for mirroring network traffic. The integration of AWS services, the utilization of the Geneve protocol, and the automation via Terraform have ensured a dynamic response to ever-changing EC2 instances. It stands as a testament to the power of cloud-based solutions to complex network challenges.